Crystal Radio Instructions
Crystal Radio

What is a Crystal Radio?
Crystal radio's were popular back in the early 1900s when the rectifying property of crystals was discovered and applied to radio receivers (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crystal_radio). Since then the crystal component has been replaced by a diode.That's where the name "crystal" radio came from. Now-a-days a better name might be the diode radio.
So, why would anyone write a hub on making a crystal radio? Because it's FUN! They are simple to put together with items you can find around the house. They do not require batteries either. Their power comes from the radio waves picked up by a long antenna. There's something intriguing about being able to make something with household junk and pick up radio waves with it.
Let's get started. The following table is a list of everything you will need to build the crystal radio.
Parts List
Parts & Tools
| Quantity
| Purpose
|
|---|---|---|
Paper Towel Tube
| 1
| This will be used to construct the capacitor.
|
Tape
| 1 roll
| For attaching wires and foil
|
Tissue Tube
| 1
| This will be used to construct the coil.
|
Magnetic Wire
| 1 spool
| This will be used for the coil.
|
Wire (blue)
| 6"
| This is connecting wires.
|
Wire (red & white)
| 12' (depends)
| The red is will be ground and the white will be the antenna.
|
Glue (super or elmers)
| 1 bottle
| Adhere objects to the board.
|
Piece of cardboard or wood
| 1 = 6" x 8"
| This will be the base for the components.
|
Screws or paper fasteners
| 3 each
| Fasten the connections
|
Helpful Tools
These are a few tools that you may, or may not, need:
- Screwdriver
- Scissors
- Wire Cutters
- Drill
- Drill Bit

Construct the Variable Capacitor
The capacitor acts like a magnet for electrons. Electrons collect on the outside foil, then move to the inside foil and back again, and again, and again. This one is called a variable capacitor because it will be telescopic, one piece sliding inside the other.
Here's how we make it:
- Take your paper towel tube and cut a piece of foil so it will wrap around it, about 7" by 5". Allow the foil to overlap itself.
- Tape it in place.
- Now take a piece of plain white paper and cut it so it will wrap around the paper towel tube. It should overlap itself.
- Cut another piece of foil so it is longer than the white paper, yet not as wide.
- Tape the foil at the ends to the white sheet of paper. Wrap the rest of the way around the tube, allow the longer end to overlap onto itself and tape to secure. Do not place tape on the length side of the foil, only on the ends.
- Slide the white paper with foil over the paper towel tube with foil. This is your capacitor.

The Coil
The coil receives the electrons from the capacitor and works with the capacitor by slowing down the electrons. The more coils, that you put on the coil, the slower the electrons will move.
Using the coated magnetic wire and the tissue paper holder, leave about a foot of leader wire and wrap the wire around the tube 100 times. For this I use super glue to hold the starting wire in place while I wrap the wire around the tissue paper. You can use tape or super glue, which ever works best for you. It's important to wrap the wire closely with as few gaps as possible.
Your Board Should Look Like One of These
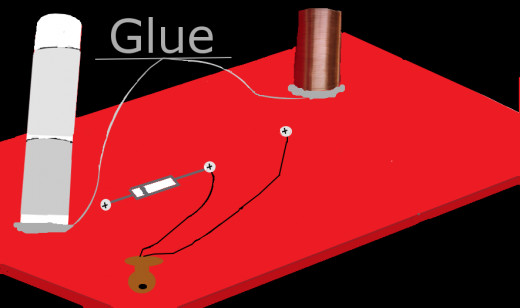
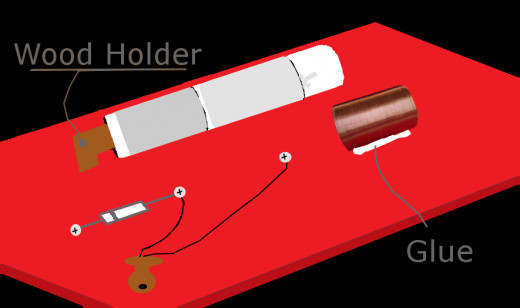
Set-up the Base
You'll need something to put the parts onto. Let's construct a base.
- A piece of scrap cardboard or wood will do fine. It should measure somewhere in the neighborhood of 6" x 8".
- Now set-up where the connections are going to be. Using either three (3) small screws or three (3) paper fasteners attach them to the board, all three in a row. If you opt for a wood base then make sure you pre-drill the holes or the wood may split.
- Attach the diode between the first and second screw/paper fastener.
- Expose the wire, on each of the two wires of the earphone and connect them to the second and third screw/paper fasteners.
- Attach the capacitor and the coil to the base board in a fashion convenient for you. Two different set-ups pictured.
Capacitor Wires
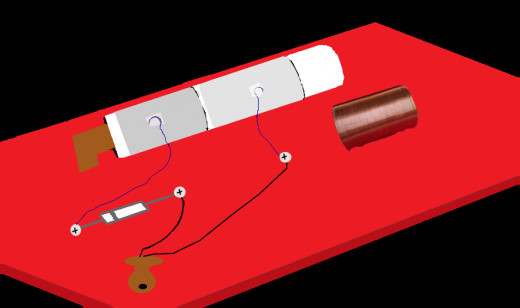
Add Wires to the Capacitor
Now it is time to attach wires to the capacitor.
- Take two pieces of wire about 6" long.
- Expose 1/2" wire at each end.
- Bend one end of each wire into the shape of a hook.
- Take a 1" piece of tape and tape the hook onto the foil at one end of the capacitor (the stationary foil).
- Get another piece of tape and tape the other hook to the other end of the capacitor (the sliding piece attached to the paper).
- Attach the other end of that wire to the third (3) screw/paper fastener.
- Attach the other wire from the capacitor to the number one (1) screw/paper fastener.
Coil Wires
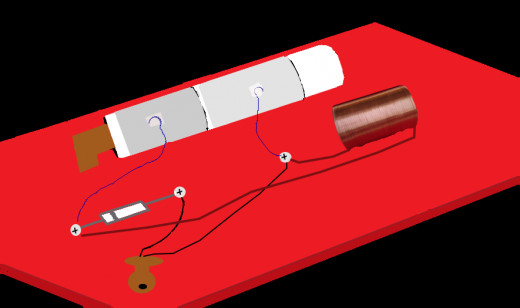
Add the Coil
Now it's time for the coil to be attached.
- On the extra lengths of wire we allowed for the coil, scrap off the very ends to remove any enamel coating.
- Attach one end to screw/paper fastener one (1) and the other to screw/paper fastener three (3).
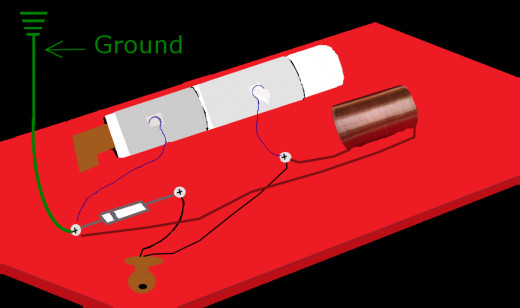
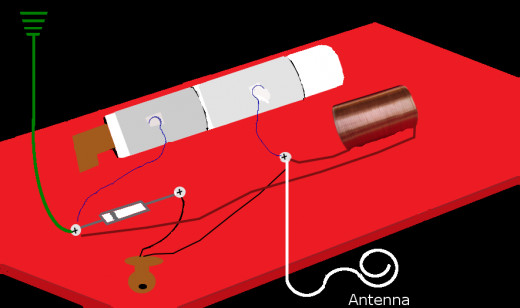
Final Steps
The final steps include attaching the ground and the antenna.
The ground can be attached to any source of ground such as water pipes under your sink, metal case of a computer that is plugged in, ground tong only on a plug, etc. The other end will attach to the third (3) screw/paper fastener.
The antenna needs to be long to give it the best opportunity to pick up sound waves. Hang it from the ceiling or across the room. Attach the other end of the antenna to the first (1) screw/paper faster.
Put the ear phone into your ear and slide the outer foil on paper, of the capacitor along the inner foil. The foil must overlap at all times or it won't collect the electrons. Listen carefully for any transmissions you can pick up!
How Many Stations Did You Pick Up
How many stations were you able to pick up?
© 2014 Joanna